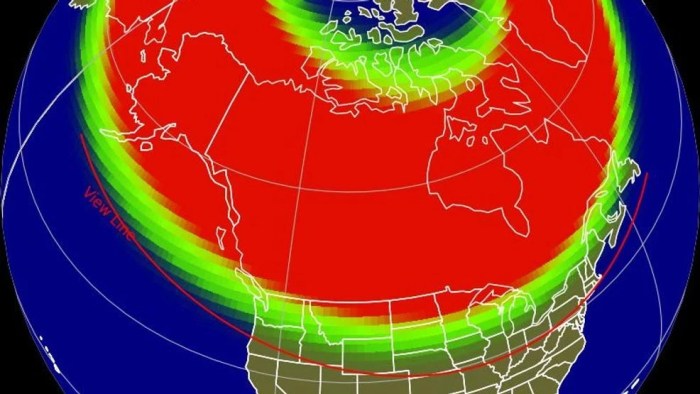
The Northern Lights are caused by the interaction of charged particles from the sun with Earth’s atmosphere.
As these charged particles enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules of oxygen and nitrogen. These collisions cause the atoms and molecules to become excited, and when they return to their normal state, they release energy in the form of light.
While you’re checking the Northern lights forecast for tonight, you might also want to keep an eye on the latest Android news. Nothing OS 3.0 Beta: Android 15 Timeline Revealed offers a glimpse into the future of mobile operating systems, potentially impacting how we interact with our devices, much like the aurora borealis captivates us with its mesmerizing dance across the sky.
So, whether you’re gazing at the celestial display or the latest tech advancements, remember that both offer a unique and captivating experience.
This light is what we see as the Northern Lights.
The Colors of the Northern Lights
The colors of the Northern Lights are determined by the type of gas that is excited and the energy level of the collision.
- Greenis the most common color, produced when excited oxygen atoms release energy. This color is typically seen at lower altitudes, around 60 to 150 miles above Earth’s surface.
- Redis often seen at higher altitudes, around 150 to 600 miles above Earth’s surface, and is caused by excited oxygen atoms releasing even more energy.
- Blueand violetare rarer colors, caused by excited nitrogen molecules. These colors are typically seen at lower altitudes, around 60 to 150 miles above Earth’s surface.
History and Cultural Interpretations
The Northern Lights have been observed and interpreted by cultures around the world for centuries.